Let’s dive into the world of online content writing jobs! If you’re wondering whether there’s a market for content writers, the answer is a resounding yes. Content writers are in high demand these days, and you might be surprised at the income potential (content-writer-jobs)
Check the popularity of the term content writing on Google and that should give you an indication.
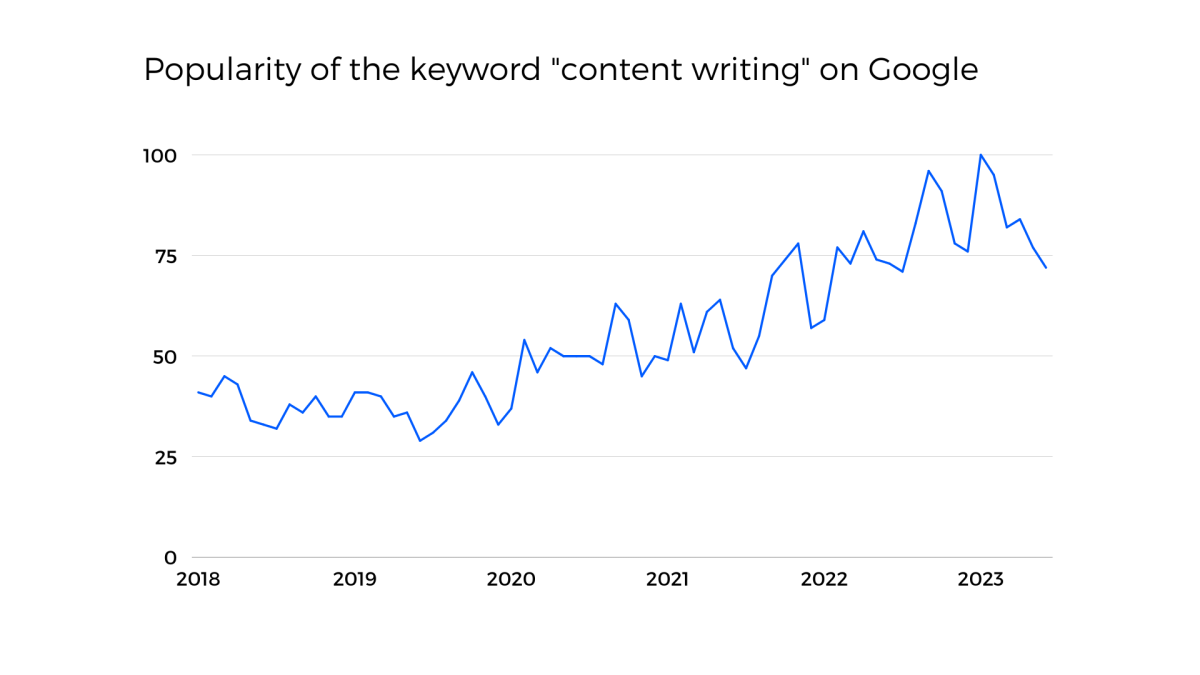
In this post let’s explore some exciting job titles that fall under the content writing umbrella:
Content Writer:
A content writer is the storyteller of the digital age. They craft engaging articles, blog posts, and other long-form content that captivate readers. For instance, a content writer for a travel website might create a piece titled “10 Must-Visit Destinations for Adventure Enthusiasts,” igniting wanderlust in their audience.
“Words can transport readers to distant lands and evoke powerful emotions.”
Copywriter:
Copywriters are the persuasive wizards of writing. They use their magic words to inspire action. Imagine a copywriter crafting a compelling product description: “Unleash Your Creativity with Our Innovative Art Supplies – Order Now and Elevate Your Artistic Journey!”
“Copywriting is the art of transforming words into irresistible invitations.”
Copy Editor:
In a world of digital noise, copy editors shine as the guardians of clarity and correctness. They meticulously review and refine content to ensure it’s polished and error-free. A copy editor might enhance a sentence like, “Our product offers quality, durability, and affordability.”
“A single misplaced comma can change the entire message; copy editors bring precision to words.”
Content Strategist:
Content strategists are the architects of storytelling. They conceive brilliant content ideas tailored to specific audiences. Imagine a content strategist devising a content plan for a fitness brand: “Motivational Monday: Inspiring Stories of Transformation and Success.
“Content without strategy is like a ship without a compass; content strategists chart the course.”
Technical Writer:
Technical writers are the translators of complexity. They distil intricate concepts and software instructions into clear, understandable guides. Consider a technical writer explaining how to troubleshoot a smartphone issue step by step.
“Simplifying the intricate, technical writers make technology accessible to all.”
Content Manager:
Content managers are the conductors of the content orchestra. They oversee a publishing team, making sure the right content takes the stage.
A content manager could lead a discussion on topics like “Navigating Sustainability: Crafting Green Living Guides for the Modern Eco-Warrior.”
“Managing content is like curating an art gallery; each piece contributes to the masterpiece.”
Content Marketing Manager:
Content marketing managers are strategic maestros. They develop plans to promote products or services through captivating content. Picture a content marketing manager orchestrating a campaign: “Unveiling the Future: A Series of Innovative Tech Insights.”
“In the symphony of marketing, content marketing managers compose harmonious melodies of engagement.”
Blogger:
Bloggers are the authentic voices in the digital realm. They share personal perspectives, insights, and expertise. A blogger might explore “The Art of Mindfulness: Navigating Life’s Chaos with Calmness and Clarity.”
“Blogging is the canvas where personal experiences blend with universal truths.”
Conclusion-
As a content writer there are many content writing jobs online that one can choose from. It depends on your skill set, experience and expertise.
Freelance content writer or in-house writer is a choice one can make based on financial goals, creative aspirations and availability of time.
Thanks for this article. I was always confused about what roles should I apply to. I have knowledge about most of the roles through my certification courses.
Thank you for the feedback
Pingback: Difference between copywriting and content writing